Literacy: Foundations For Learning.
Literacy underpins the school curriculum by developing students’ abilities to communicate verbally and non-verbally, access written information as well as reading for pleasure. The acquisition of these skills is vital to students’ development across the curriculum and to function independently and successfully in the wider world. The development of these fundamental skills supports learning and achievement across the curriculum and it is the responsibility of teachers and support staff from all subjects and Key Stages to ensure that students are able to access the right of literacy.
Sound literacy skills are essential for progress across the curriculum and to enable students to function effectively in adult life.
Literacy is fundamental for success in school and later life. Students who cannot read, write, and communicate effectively are highly unlikely to access the challenging academic curriculum in secondary school and are more likely to have poor educational outcomes across all subjects. As the stats below suggest reading is a super power which needs to be enhanced!
• The average GCSE paper has a reading age of 15 years and 7 months…
• The average GCSE student has a reading age of 13 years…
• In Year 3 students read an average of 36 books a year…
• By Year 10 this is an average of 5 books a year…
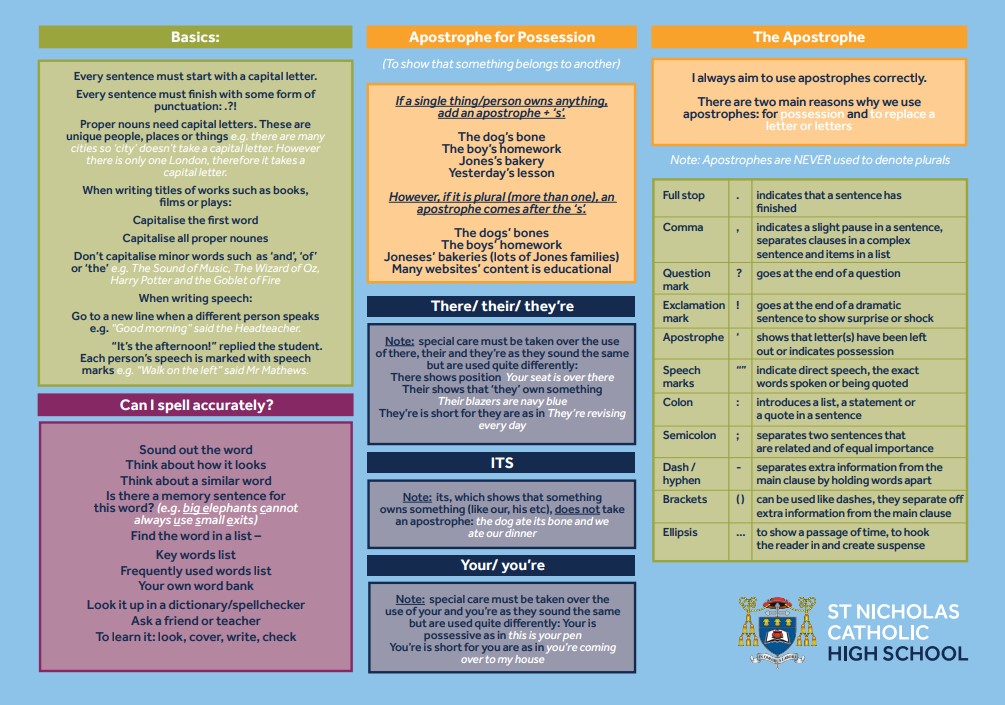
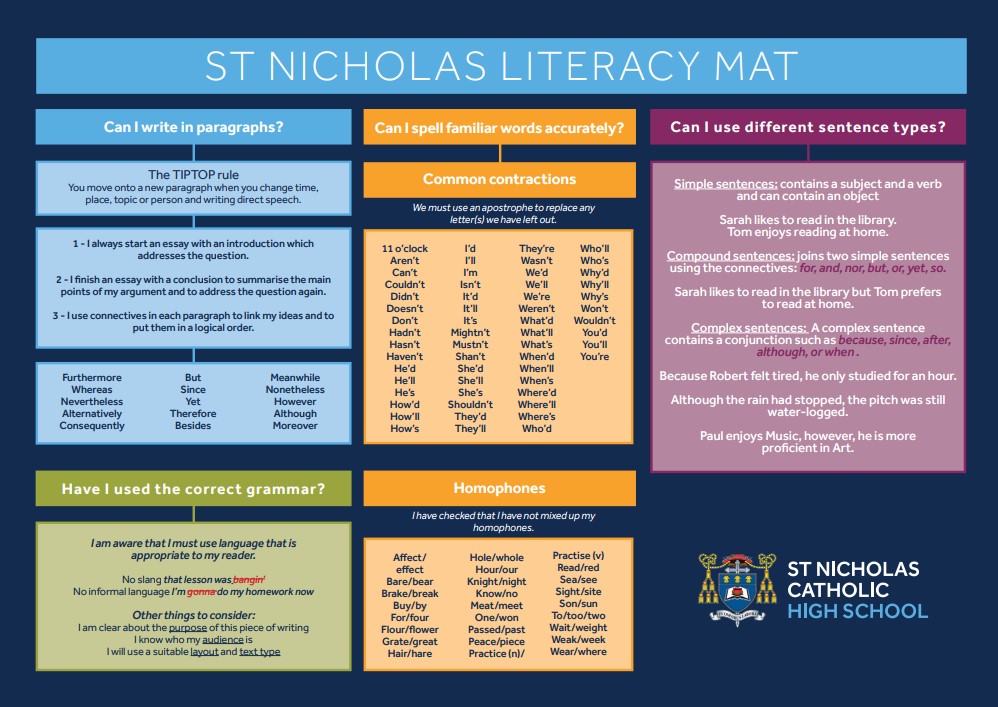
Below are the various strategies we are implementing.